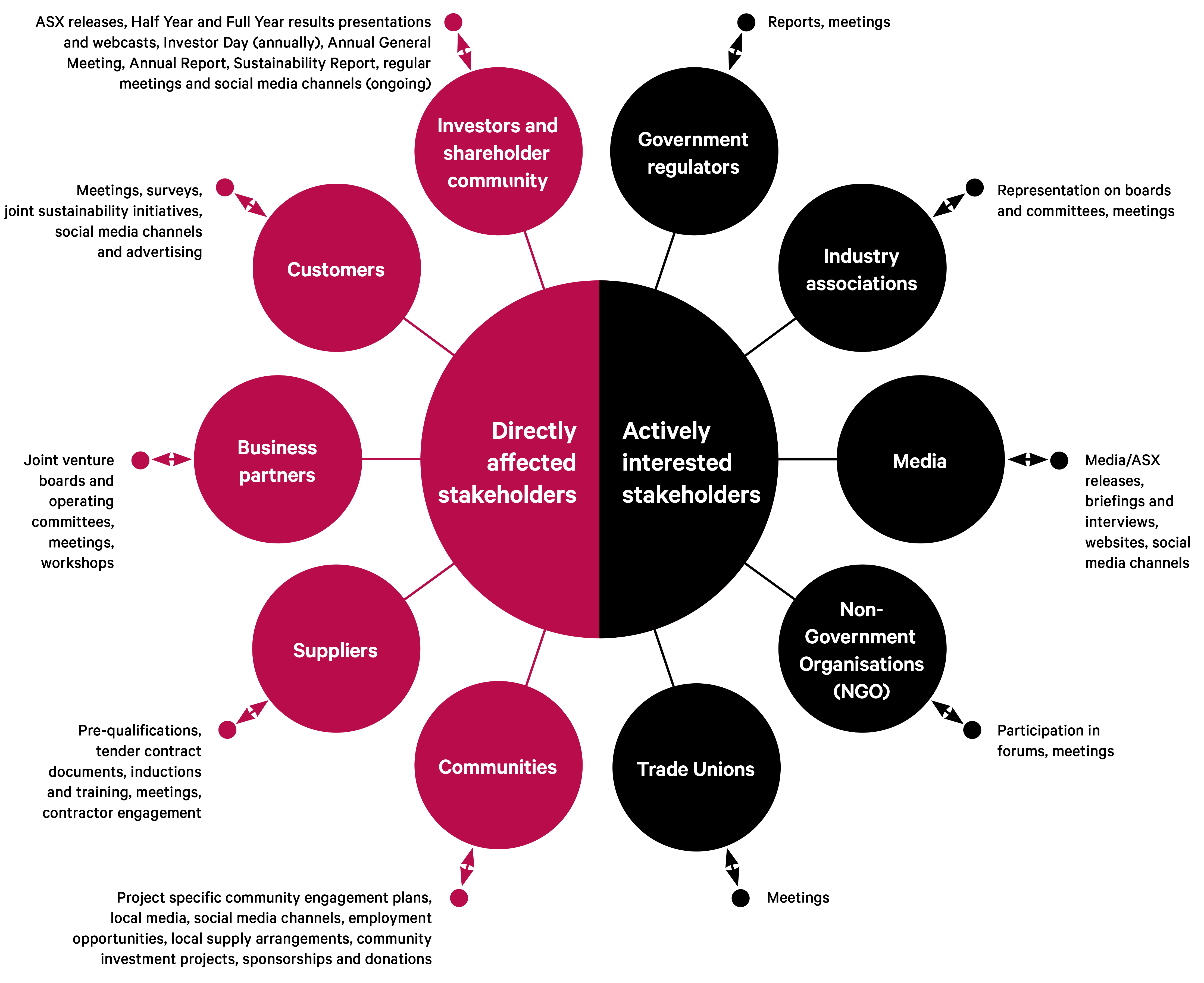
Our stakeholders
Downer recognises that our business operations have a direct impact on a wide range of stakeholders.
Downer believes that what is important to our stakeholders is important for us to meet our strategic objectives and fulfil our Purpose. This requires ongoing and effective engagement with our stakeholders, where we provide transparent and timely information and actively encourage feedback. We utilise the following initiatives to promote open, two-way communication between Downer and our stakeholders.
What are material issues?
Downer seeks to identify the issues that matter most to the business and its stakeholders, and have the greatest potential to impact our future success and returns to shareholders. We refer to these as our material issues. This year, Downer revisited its materiality assessment in accordance with the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) Standards. Independent expert, Materiality Counts, led a process to engage internal and external stakeholders to identify and understand our material economic, social, environmental and governance risks and opportunities.
Why we do this
Materiality helps Downer to focus its sustainability reporting on the most important issues, helping to keep it directly relevant to what matters to our stakeholders. Material issues are also a valuable input to our strategic planning. Downer recognises these issues may change over time, reflecting changes in our business and external operating environment and the expectations of stakeholders. We use the results of the materiality assessment to inform our business strategy thinking and our sustainability framework and targets. One example is our alignment to the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) and setting a long-term greenhouse gas (GHG) emission reduction target. Another example is our People strategies that focus on retaining and attracting talent in a highly competitive market for skilled labour, and the setting of gender diversity targets.
Our materiality process
The independent process consisted of the following three steps:
Step 1
Potential material issues list:
A list of potential material issues, alongside short explanations, was compiled using a comprehensive range of inputs from various stakeholders, as mentioned above. These included material risks, media scanning, stakeholder feedback, employee surveys, peer review, industry trends and the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This resulted in a consolidated list of 18 potential material issues for review and discussion by stakeholders.
Step 2
Materiality survey:
A representative sample of stakeholders was identified for consultation on the relative importance of these issues. This included internal stakeholders – namely Board members, Executives and employees – as well as external stakeholders including investors, business customers, suppliers, industry associations and Non-Governmental Organisations (NGOs), ensuring geographic spread across Australia and New Zealand. All 24 stakeholders identified completed a survey providing quantitative data on the relative priority of the issues.
Step 3
Stakeholder interviews:
One-on-one telephone interviews were undertaken with selected external stakeholders which provided qualitative context to inform our understanding of the current and future context of each issue, including the potential for it to impact our value creation over time.
Materiality results
This year, stakeholders prioritised the issues based on their importance for Downer. More specifically, the issues’ importance in terms of the impact Downer has, which Downer should therefore prioritise. An overall issue ranking greater than 8.20 (sum of the average internal and the average external rankings) has been taken as the materiality threshold for Downer. This provided a list of the top 11 issues which Downer deems to be its material issues. The remaining seven issues, which remain important to Downer and will continue to be managed, are referred to as other issues.
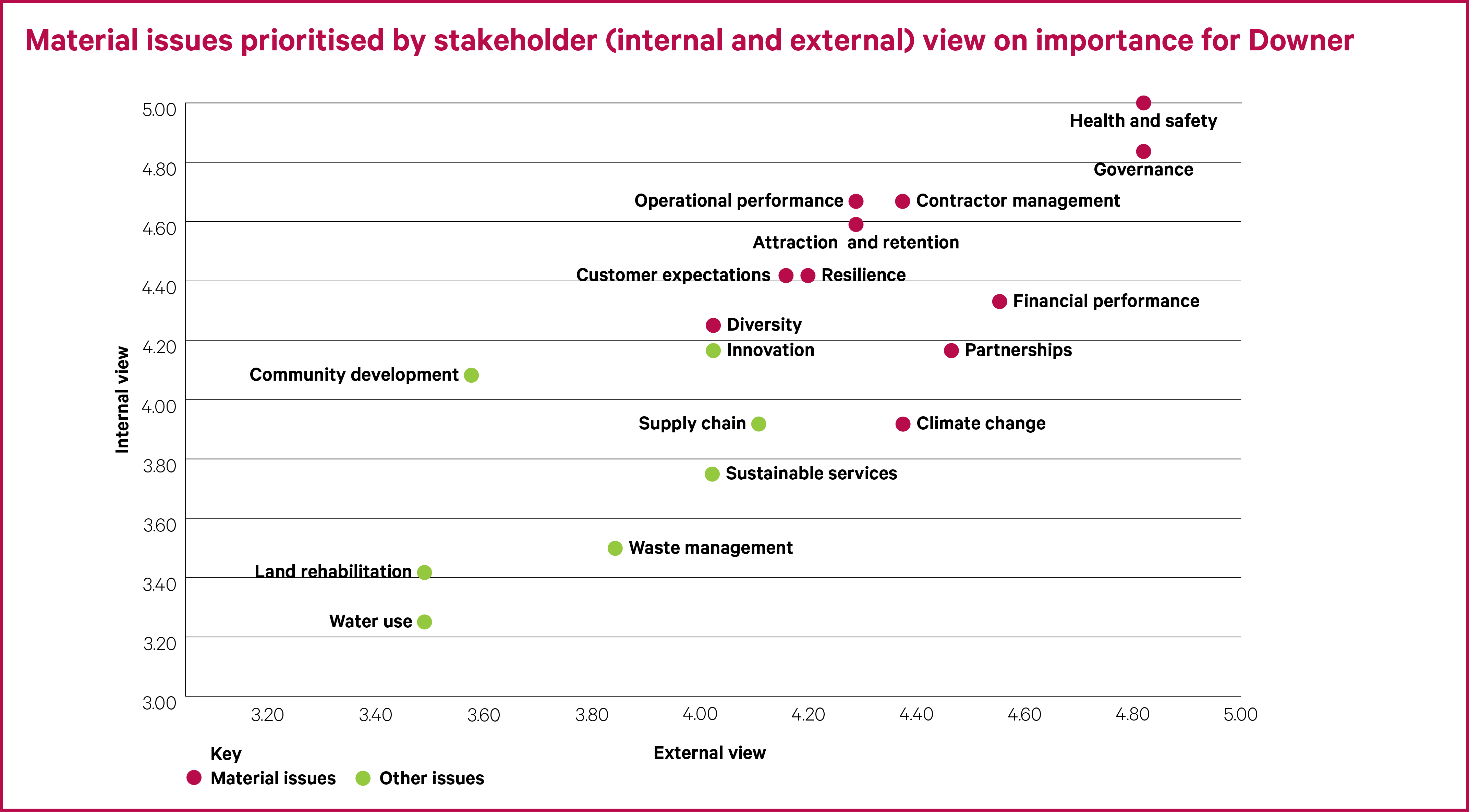
Material issues
This materiality assessment identified a prioritised list of 11 material issues and the context behind each are as follows:
The material issues identified above are addressed within the relevant sections of this Sustainability Report, except for financial performance, operational performance and business resilience. Instead, these are referenced within the context of the Sustainability Report but addressed in more detail in Downer’s Annual Report.
The other issues, in order of priority are:
Changes from previous years
This year Downer has considered a broader list of material issues and used the materiality assessment process described to engage directly with a representative sample of stakeholders to rank and prioritise its material issues. This has resulted in Customer Expectations being included and Community Development excluded from Downer’s material issues list. Despite this change, Downer acknowledges that the communities in which we operate are key stakeholders.
UN Sustainable
Development Goals
In 2015, the United Nations agreed on 17 SDGs as part of a 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development to end poverty, promote prosperity and wellbeing for all, and protect the planet.