Our approach
Downer and our stakeholders place a strong importance on governance and ethical conduct. This was reinforced in the outcomes of our materiality assessment, where governance and ethical conduct ranked as Downer’s second-highest priority issue.
Downer’s approach to sustainability is underpinned by a robust corporate governance framework. This framework provides the platform from which Downer’s Board provides strategic direction for the responsible and sustainable growth of the company. It also drives a culture that promotes high ethical standards and personal integrity.
Under our governance framework, Downer’s management is accountable to the Board, and the Board is accountable to shareholders for the operations, performance and growth of the company. The primary goal the Board has set for management is to focus on enhancing shareholder value, which includes responsibility for Downer’s economic, environmental and social (ESG) performance.
Our Board recognises the need for the highest standards of behaviour and, as such, endorses the ASX Corporate Governance Council’s Corporate Governance Principles and Recommendations (ASX Principles). Our Corporate Governance Statement for the year ending 30 June 2021 is included in our Annual Report.
Ensuring our governance and ethical standards are adhered to by our diverse supply chain remains a challenge, particularly around issues such as human rights and modern slavery, and data security.
Read moreOur performance
Downer committed to achieving the following governance targets and objectives in the 2021 financial year.
The performance information in this section includes Australian Operations, Spotless and New Zealand, including Hawkins. While Downer’s governance policies and procedures cover contractors and joint ventures, performance information in this section excludes these entities.








Significant progress was made this year in delivering on focus areas that were disclosed in Downer’s 2020 Sustainability Report. Downer’s key focus areas during the year were to:
Board Structure
We appreciate the value of diversity on our Board and this is taken into consideration during the appointment process.
Read moreBoard committees
The names of the members of each committee are included in Downer’s 2021 Annual Report.
Organisation structure
In June, Downer announced an important organisational change to improve operational alignment and performance.
The new role of Group Chief Operating Officer was established, tasked with improving Downer’s project, contract and operational performance and with bringing together Strategy, Growth and Innovation, People and Culture, The Downer Standard, Tenders and Contracts Committee and support for the Board Tender Risk Evaluation Committee.
This role is an important addition to the way we will manage and govern the Downer Group.
It will align the key functional areas responsible for our core management system and its successful implementation. Improvement in our project and contract margins is a key goal for the Group, with high level conformance to The Downer Standard’s Delivery Management Methodology being the most important enabler.
Peter Tompkins, who was Downer Group General Counsel and Company Secretary from 2010 to 2018 and Spotless CEO from 2018 to 2021, has been appointed to the new role of Chief Operating Officer, reporting to the Group CEO. Peter has made significant contributions to Downer’s risk and governance processes, which will continue to be a focus in this new role.
Internal audit and risk
In FY21, Downer’s Internal Audit and Risk function completed 21 internal audits comprising seven project reviews and 14 reviews of key business processes. The audits and reviews that relate to Downer’s material issues consisted of:
- Plant management: This review was focused on efficient and timely management of Downer’s plant maintenance activities. The audit confirmed maintenance was performed in a timely manner, ensuring the reliability and optimal performance and safety of the plant, and minimising greenhouse gas emissions from a poorly maintained plant. The review did not identify any matters associated with untimely maintenance.
- Procurement: The review encompassed modern slavery management processes, in particular ensuring our contractual conditions associated with modern slavery were appropriately identified and complied with. Minor matters identified were addressed.
- HCMT engineering change control: Review confirmed Safety Plans associated with the HCMT build met the regulatory requirements. The audit identified no issues.
- Project reviews: Eight individual project reviews were conducted. Each assessed the project’s processes in accordance with The Downer Standard to manage risk including safety and environment requirements.
Downer is committed to ensuring its employees are paid in accordance with their employment agreements and its legal obligations. Downer is nearing completion of a major review of applicable Enterprise Agreements and Modern Award obligations in the Spotless business to calculate, validate and, where necessary, remediate any historical underpayment. As at 30 June 2021, Downer was carrying a payroll remediation provision of $3,093,720 and an additional provision for contrition of $1,200,000.
Tenders and Contracts Committee
The Tenders and Contracts Committee (TCC) is a Downer Group management committee which is central to Downer’s bid and risk management, making recommendations to the Group CEO on EOIs, Bids and Projects reviewed in accordance with its Opportunity and Bid and Delivery Management procedures.
Standards of Business Conduct
Downer’s Standards of Business Conduct and related Policies are available on the Downer website.
In FY20, Downer reviewed its Standards of Business Conduct and made a number of important changes.
In FY21, Downer continued to roll out our Standards of Business Conduct training and Workplace Behaviour training, with 16,550 employees completing the modules.
Financial and Corporate Governance Self-Assessment
Downer conducted two Financial and Corporate Governance Self-Assessment (FCGSA) surveys in FY21, with 311 senior executives completing the first, and 278 completing the second, both of which had 100 per cent completion rates.
Timely, honest and transparent disclosures
In FY21, Downer made 79 announcements and disclosures via the ASX and NZX. Of these, 13 were Director’s interest disclosures and 14 related to Downer’s On-Market Buy-back
which was announced on 27 April 2021. There were no breaches of continuous disclosure and Downer is unaware of any substantial complaints regarding breaches of privacy or other matters by customers or other stakeholders.
Political donations
In FY21, Downer made a total of $7,449 in political donations to the major parties through participation in industry forums. Donations were made to the WA Labor party ($4,949) and the Liberal National Party ($2,500).
Insider trading
There were no reported breaches of the Securities Trading Policy in FY21.
Anti-competitive behaviour
There were no breaches or litigation associated with anti-competitive behaviour brought to Downer’s attention in FY21.
Anti-bribery and corruption
There were no breaches or litigation associated with anti-bribery and corruption brought to Downer’s attention in FY21.
Whistleblower management training
In FY21, Downer strengthened our governance of business integrity by developing and launching a training module on Downer’s policies and practices for the management of whistleblower reports. 486 employees completed the training in FY21.
The Downer Standard
The materiality assessments that Downer undertake consistently rank governance as one of our most important material issues. One of the key strategic initiatives to strengthen Downer’s governance is The Downer Standard.
The Downer Standard (TDS) is a Downer-wide Integrated Management System that underpins our approach to serving our customers, managing our processes, meeting our business obligations, and continually improving what we do. It covers the breadth of our core business processes including Asset Management, Customer Planning and Engagement, Finance, Information Technology, Legal, Opportunity and Risk, Procurement, Project Management and Delivery, Commercial, and Zero Harm.
TDS is closely aligned to Downer’s Purpose, Promise and Pillars, and has been created based on input from all parts of the Downer Group, capturing intellectual property which represents best practice gleaned over many years of doing business. It has been implemented across all parts of the Downer Group.
It is more than just a set of policies, standards and procedures ensuring we fulfil the tasks required to achieve our objectives.
The Downer Standard is a vital governance tool which:
- Includes a structure for governing and sustaining our core processes and capabilities
- Is embedded into Downer project and contract processes and tools to ensure consistent service delivery
- Acts as a vehicle for sharing knowledge and best practice
- Establishes a framework for quality assurance via single certification to international management standards (ISO 45001, 9001 and 14001)
- Provides a backbone for learning and professional development
- Facilitates rapid integration of new acquisitions, mergers and joint ventures
- Enables a culture of continuous improvement and customer centricity.
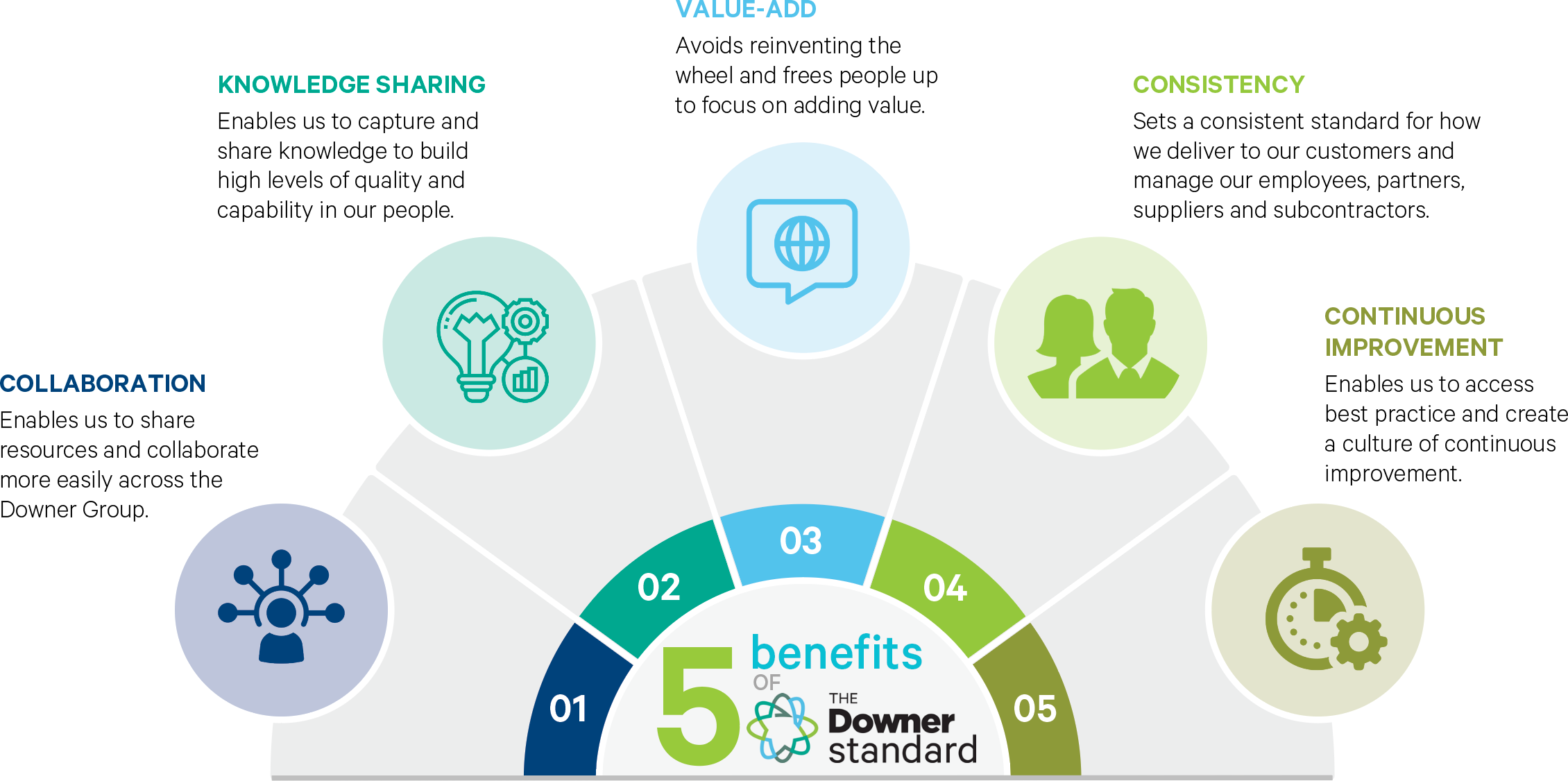
The Downer Standard project commenced in 2018, with the aim of delivering five key benefits across the Group: consistency, collaboration, value-add, knowledge sharing and continuous improvement.
The Downer Standard team has made significant progress over the past 12 months.
We have defined and launched The Downer Standard content across the Downer Group for all core processes.
We have also outlined and prioritised The Downer Standard adoption activities for all Business Units, including the embedment of The Downer Standard into all induction programs for new hires.
In an important step, Downer achieved centralised third-party accreditation to the International Standards ISO 45001 (Safety), ISO 9001 (Quality) and ISO 14001 (Environment).
This gives us a single system of work for managing environment, safety and quality and a framework to develop and monitor The Downer Standard.
In May 2021, we established The Downer Standard Leadership Team, which includes a number of senior executives. The Leadership Team has a Charter and Mandate, including an ongoing governance structure to enable continual improvement, prioritisation and oversight of TDS.
Labour practices and modern slavery (suppliers, contractors and partners)
Downer is committed to operating responsibly and establishing and adhering to the highest ethical standards.
We reject any activities which may cause or contribute to modern slavery, including forced or bonded labour, child labour, human trafficking, slavery, servitude, forced marriage or deceptive recruiting for labour or services.
Ensuring that modern slavery is not taking place in Downer’s workforce, which includes our supply chain beyond our direct suppliers, is challenging given the diversity of our service offerings and locations.
However, Downer has designed and implemented a risk-based approach and is committed to continuously improving our processes. This includes engaging with our direct suppliers to educate, assess and encourage improvement in their own capacity to manage modern slavery risks within their broader supply chains.
On 10 February 2021, Downer released our first Modern Slavery Statement, which is available on our website.
The statement outlines our approach to address and minimise the risk of modern slavery in our business operations and supply chains.
Downer is committed to releasing our Modern Slavery Statement by 31 December annually, which will span the previous financial year ended 30 June. This is supported by our Group-wide Procurement Framework Policy and Standards of Business Conduct. These policies are supported by the following:
- Procurement induction and training module
- Supplier and subcontractor prequalification
- International Supply Standard – for international supply
- Standard precedent terms and conditions for all supply agreements and subcontracts, including our purchase order terms and conditions
- FCGSA Directors’ questionnaire
- Downer’s risk assessment process.
Downer’s risk assessment process sets a base level identification of modern slavery risk by considering country risk, and product/service category risk.
To improve our understanding of local human rights contexts, as well as exposure to related issues such as corruption, we use tools including the Global Slavery Index. The majority by value of our payments are made to goods and services suppliers in Australia and New Zealand, primarily in lower risk categories such as skilled subcontractors, fleet, fuels and professional services.
We recognise there is risk; however, it is primarily in our lower category spend areas and products sourced from countries with a higher risk of modern slavery. For example, Downer works with suppliers in China through its partnership with CRRC Changchun, which is delivering Sydney’s Waratah trains and Melbourne’s new High Capacity Metro Trains.
One of CRRC’s suppliers for the High Capacity Metro Trains was the subject of public allegations in 2020, concerning the treatment of their workforce with respect to human rights and modern slavery. These allegations have been denied strongly; however, incidents like this highlight the challenges Downer faces in managing these issues outside of our immediate supply chain.
While there are potential benefits and cost savings associated with overseas sourcing, we need to consider the risks which include:
- Additional costs for international administration, foreign currency exchange, transport and customs duties
- Logistical challenges including import, customs and quarantine regulations
- Exposure to modern slavery and potential for bribery and corruption in some foreign jurisdictions
- Limited legal protections in foreign jurisdictions, should disputes arise
- Increased rules and regulations in foreign markets and dealing with foreign entities
- Language barriers and understanding of foreign supply market
- Differences in quality and safety standards.
To further enhance our risk assessment process, Downer is currently conducting specified testing for a sample of international procurement activities.
Downer also proactively works with our supply chain to support social and sustainable outcomes, including reducing the risks of modern slavery impacting Downer’s supply chain.
External consultation: Relationships and collaboration with our suppliers, business partners and relevant agencies help shape our strategies on modern slavery. We have actively participated in relevant forums to discuss and understand peer, industry and stakeholder views on human rights issues including modern slavery. These forums include:
- Infrastructure Sustainability Council of Australia Modern Slavery Coalition
- Business Council for Sustainable Development Australia
- Procurement and Supply Australasia Connect
- Supply Chain Sustainability School.
We are committed to continually moving forward to ensure the prevention of modern slavery through operational and supplier-driven processes across our value chain. We will continue to collaborate with our internal and external stakeholders to address our own modern slavery risks and continue to improve our processes. Several of our processes will help track our performance and will provide insight into areas for improvement.
Setting the Standard
Industry memberships and associations
Downer is a member of various peak industry bodies and organisations which influence policies on sustainability across industries.
READ MORE
Some of these include:
- Australian Constructors Association (ACA) – including Board representation
- Australian Industry Group
- Business Council for Sustainable Development Australia
- Business Council of Australia
- Civil Contractors Federation
- Clean Energy Council
- Group of 100
- Infrastructure Partnerships Australia
- Infrastructure Sustainability Council of Australia
- Institution of Professional Engineers New Zealand
- Responsible Construction Leadership Group
- Supply Chain Sustainability School
- Sustainable Business Council of New Zealand.
Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a major global challenge across industry and government.
Downer maintains an information security risk management program, in accordance with its Group-wide Risk Management Standard, which is aligned to the principles of ISO 31000. Cyber and information security risks are reported to both the Board and the Audit and Risk sub-committee on a quarterly basis.
READ MORE
In addition to the security implications of COVID-19 and remote working, cyber activities against government entities, large private companies, third-party contractors and supply chain organisations have become increasingly sophisticated and targeted. In conjunction, there has been marked increase in frequency, sophistication and scale of ransomware incidents over the past 12 months.
Downer takes its obligations around cybersecurity seriously and has been actively maturing its practices through the delivery of the cybersecurity roadmap and strategy.
However, we are not immune to cyber threat. In FY21, Downer experienced a cyber incident involving a data breach that was notifiable to the Office of Australian Information Commissioner (OAIC). The incident occurred in October 2020 and involved a ransomware incident where an unauthorised third party gained access to our Spotless business’ IT network.
In response to this event, Downer enacted its security incident response program, which included the engagement of our forensics specialists, and the initiation of Business Continuity Plans. We notified the Australian Cyber Security Centre and, with support from key strategic providers, were able to contain the threat, restore networks and recover critical business services.
Downer’s focus remains firmly on continuously protecting the organisation from harm against evolving cyber risks and threats, demonstrating credibility and trust through secure cyber stewardship and custody, and supporting the maintenance of the organisation’s risk appetite through cost-effective measures. Downer has established accelerated cyber risk mitigation programs to support this focus. Over the coming 12 to 18 months, these programs will deliver:
- Revised security strategy and roadmap that reflects the current threat landscape, captures learnings from recent incidents and meets our IT and business needs, risks and priorities
- Matured security capabilities, and the implementation of a new security operating model that includes new roles and processes – this is a key learning from the recent security incidents
- Enhanced operational resilience via implementation of the recommendations and learnings from security incident reviews, including remediation of vulnerabilities in our environment as a result of legacy technology and assets
- ISO 27001 Information Security Management System compliance and drive compliance with the Essential Eight strategies to mitigate cybersecurity incidents.
We also recognise our responsibility within our supply chain, and will continue to work closely with our partners, critical asset owners and customers to maintain confidentiality and integrity.
Business resilience
The impacts of COVID-19 have resulted in a sharpened focus on business resilience, or an organisation’s ability to withstand a crisis.
Downer’s business model has remained resilient throughout the COVID-19 crisis.
READ MORE
Downer’s Urban Services strategy seeks to maintain this resilience by focusing on businesses with predictable revenues, cash flows and attractive medium-term and long-term growth opportunities. Downer’s divestment from Laundries and sections of our Mining business aligned with our Urban Services strategy to focus on capital-light sectors.
Downer’s Business Resilience Plan and Business Continuity Plan guidelines have been refined over the past 18 months. In a specific response to the pandemic, a COVID-19 Standard and Pandemic Playbook were developed and continue to be implemented.
The Downer Board also reviews the Group risk profile twice each year, inclusive of business resilience.
Business resilience is more than just financial resilience – it relates to the resilience of our people, systems and relationships. We are committed to continue building the resilience of both our business and our people. Downer rolled out its Group Health function in 2018, and in FY21 the team has continued its core focus on promoting good mental health across the Group, through the provision of the Mental Health First Aid program and other initiatives. Downer has continued its focus on flexible working, where possible, throughout the COVID-19 crisis, and has spent considerable time and investment equipping our systems and employees/contractors with the tools to enable efficient flexible work.
Sustainability performance related remuneration
Downer’s remuneration framework for key senior employees has been successful in creating alignment between senior Executives and shareholders.
Executive remuneration has a fixed component and a component that varies with performance. Performance is assessed annually for performance periods covering one year and three years. Payment for performance assessed over one year is a Short-Term Incentive (STI). Payment for performance over a three-year period is a Long-Term Incentive (LTI).
Safety
Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate (TRIFR)
Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR)
- Achieve TRIFR and LTIFR below the defined threshold for area of responsibility.
- Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR) <0.9
- Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate (TRIFR) <3.50
- Spotless: Lost Time Injury Frequency Rate <1.05 and Total Recordable Injury Frequency Rate of <3.5.
Zero Harm leadership (safety and environment)
- No actions arising from High Potential incidents overdue >30 days.
Critical Risks (safety and environment)
- Business Units to undertake a review of all Critical Controls for two Critical Risk activities, selected from the company’s top five activities. Business Units to develop plans to raise the effectiveness for the five least effective Controls from each of these Critical Risk Activities (total of 10 Controls).
Sustainability and GHG emissions reduction
- Business Units to undertake a materiality assessment and identify two material Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Develop an Improvement Plan for the top two material SDGs and achieve the first-year goals as determined by the two improvement plans.
- Business Units to provide adequate evidence they are on track to achieve the Science-Based Target (decarbonisation), net zero by 2050.
Our future focus
Downer understands that, just as our business and customers are evolving, our governance structure must also evolve. We are committed to continuously improving our governance processes and policies to ensure the highest standards of corporate behaviour. In FY22, Downer will:
- Continue to maintain and strengthen our governance of business integrity
- Undertake a significant redesign of Downer’s Risk Appetite Statements that were approved by the Board in 2016. This will require the Business Units to assess opportunities against portfolio-specific risk appetite classifications and, where they sit outside these risk appetite classifications, a formal approval process will be required
- Continue to review our labour practices and supply chain through updates to our existing frameworks, policies and processes to take into consideration modern slavery and release our FY21 Modern Slavery Statement in December 2021.
- Continue to progress The Downer Standard. This will include:
- Centralising Business Unit-specific process and capability documents within The Downer Standard
- Commencing implementation of The Downer Standard Mandate, governed by TDS Leadership Team
- Defining and implementing a standard management review process
- Launching the Delivery Governance Model app in Australia to automate and simplify adherence to the Delivery Management Methodology, a core process area within The Downer Standard.
- Revise Downer’s Privacy Policy to ensure that standards for the collection, use and disclosure of personal information are maintained
- Complete the roll-out of the training module on privacy, which will be made available to General Managers and above, as well as employees from functional areas who handle personal information as part of the responsibilities of their roles
- Continue to review our membership of peak bodies and industry associations.

